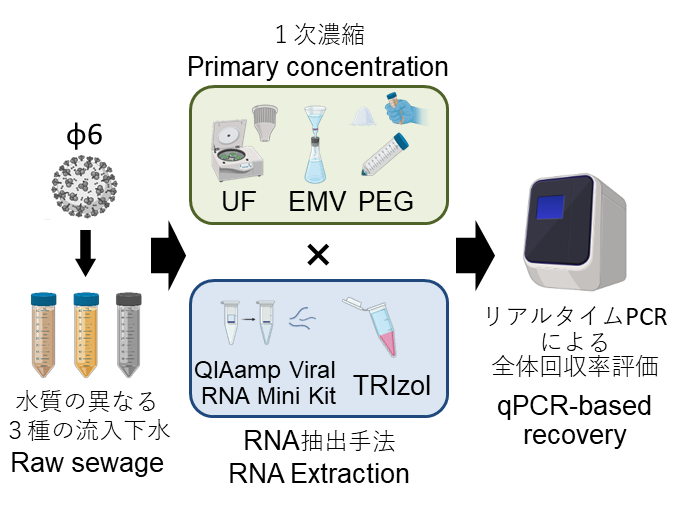
水質制御技術・素材部門
(1) ナノ構造高分子液晶膜を用いる水からのウイルスや微量有害物質の効率的除去ウイルスや有害物の無い安全安心な水の確保は、世界的に重要な課題となっています。水中の微量有害物質の効率的な除去を可能にする多孔質高分子膜を開発しています。自己組織化により形成するサブナノあるいはナノメートルレベルの孔径が揃った秩序のあるチャネルを有する液晶高分子膜を活用は、ウイルスなどを高度に除去するのに有用であることが示されています。 写真: 液晶分子が秩序だった構造になる性質を利用した、水を浄化する水処理膜 |

|
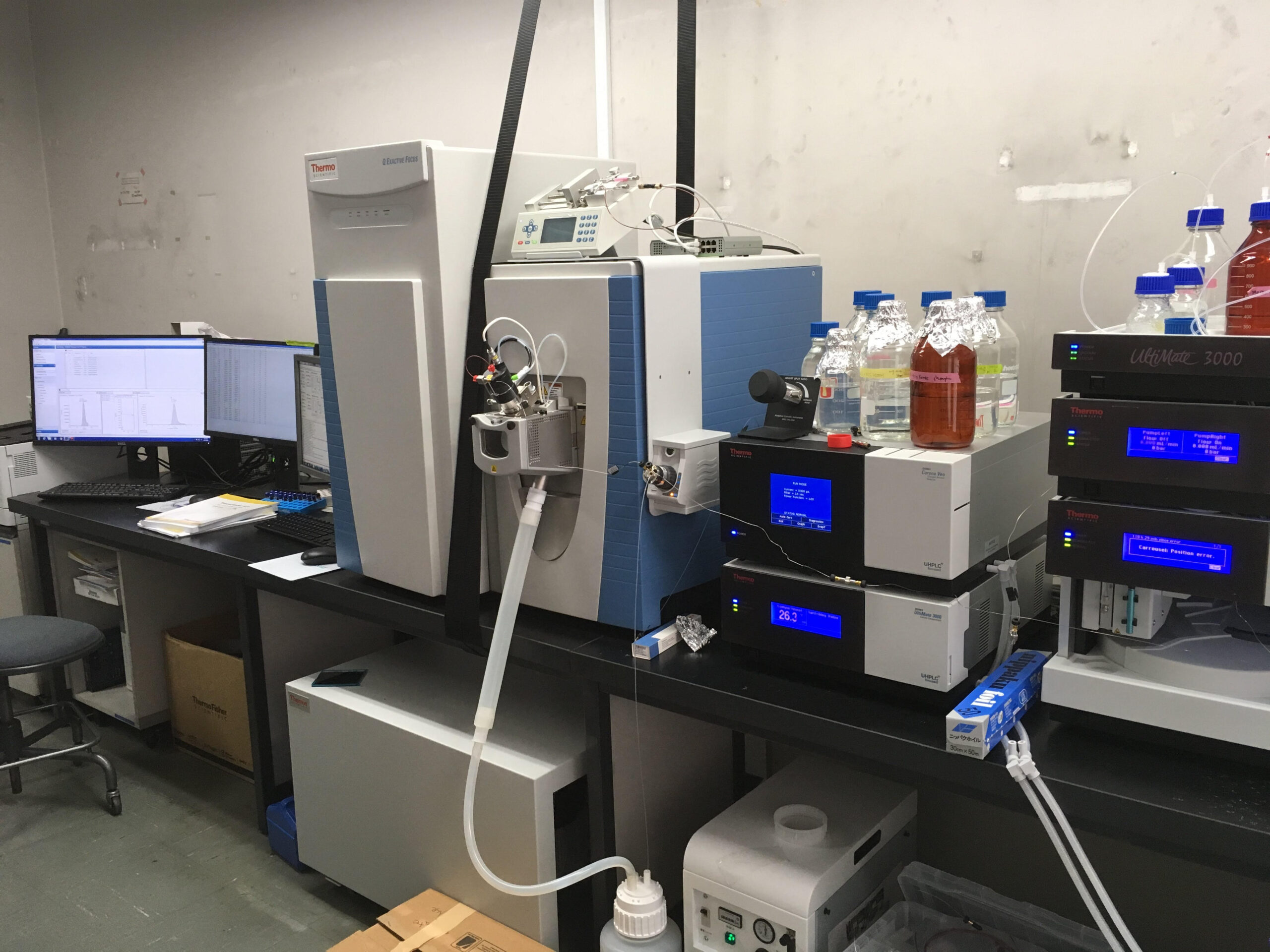
(3) 水利用を考慮した水環境中の有機物管理生活や産業から排出される多種多様な有機物は水処理を経て、天然の有機物とともに水環境に存在します。それらの一部は水利用を行う際に有害性が懸念されるほか、消毒副生成物を生成し、細菌再増殖の基質となり、水処理における障害の要因ともなっています。我々は、高分解能質量分析を用いて有機物を分子種レベルで把握することにより、未知の成分をトップダウンで追跡して各種課題の解決方法を示す研究に取り組んでいます。 写真:有機物を分子種レベルで把握するための高分解能質量分析装置 |

|
水システム管理部門
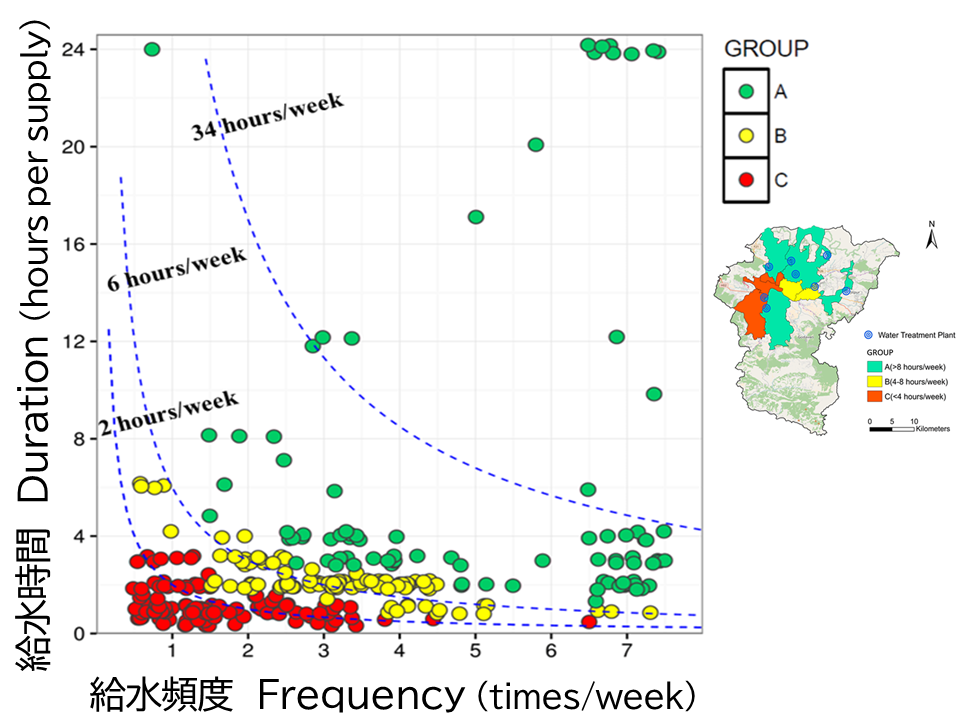
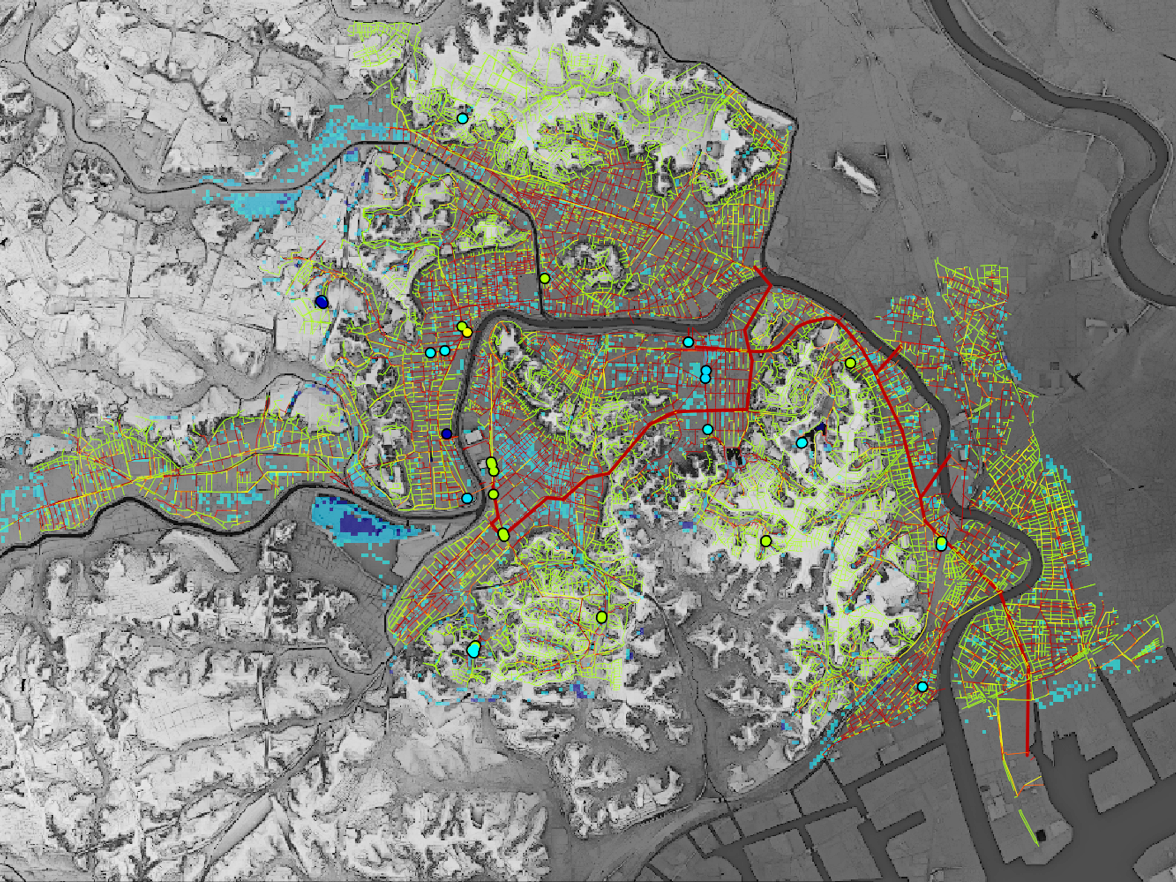
(1) 都市浸水リスクマネジメントの高度化集中豪雨の発生頻度が増加するなか、浸水対策の高度化やスマート化が求められています。そこで、高解像度レーダー雨量観測や、マンホールIoT による下水道管渠内水位のリアルタイムセンシングなどの先端技術を活用した、次世代の都市浸水予測手法の開発を行っています。そして、高精度な浸水予測情報に基づいた治水ストックを最大限に活用する方策、被害軽減のための避難行動誘導や浸水防止計画などに関する研究をしています。 画像:鶴見川低平地における河川と下水管内水位を統合的に解析する新たな都市浸水モデル |
|
(2) 都市沿岸域における雨天時汚濁現象の解明雨天時流出汚濁源には、道路交通等に由来するノンポイントソース汚濁負荷、合流式下水道雨天時越流水などが挙げられます。重金属・多環芳香族炭化水素類などの有害微量汚染物質による汚染だけでなく、受水域における糞便汚染も評価することが求められます。そこで、合流式下水道雨天時越流水由来汚染物質のモデル挙動解析や水辺空間における健康リスク評価を目的とした研究をしています。 写真:東京港沿岸域における降雨後採水調査 |
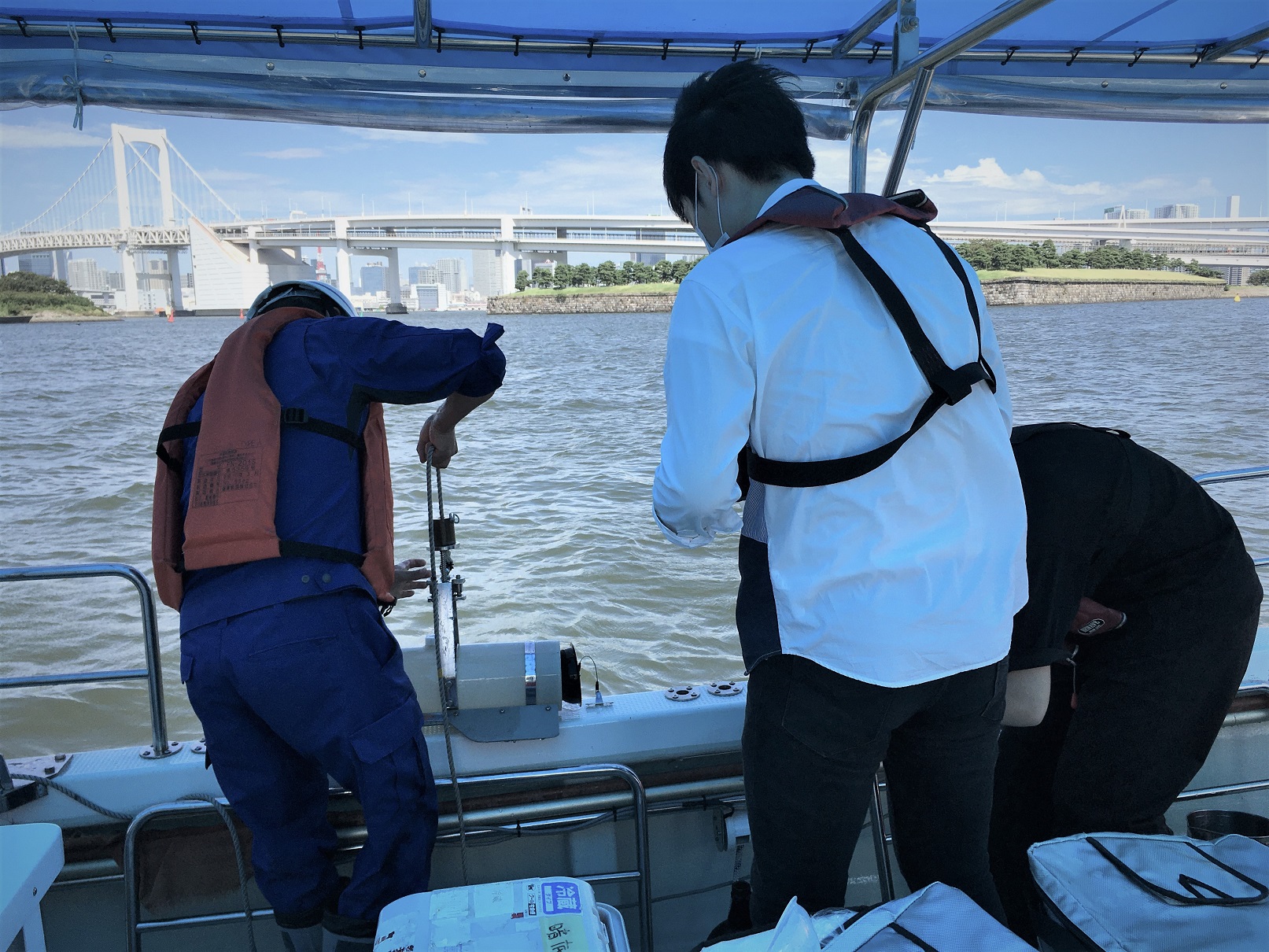

|
(3) グリーンインフラなどの雨水流出抑制対策の評価都市雨水管理において、河川改修や下水道整備とともに雨水流出を抑制する浸透・貯留施設を設置する流域対策が重要となっています。緑地空間を生かした流出抑制施設であるグリーンインフラは、魅力ある居住空間の創出、雨水をゆっくり流すことによる浸水対策の強化、地下水のかん養、市街地排水中の汚染物質の除去など、多面的な機能を有しています。そこで、流域水循環モデルを構築してその機能を定量的に評価する研究をしています。 写真:流出抑制効果を持つグリーンインフラの事例 |
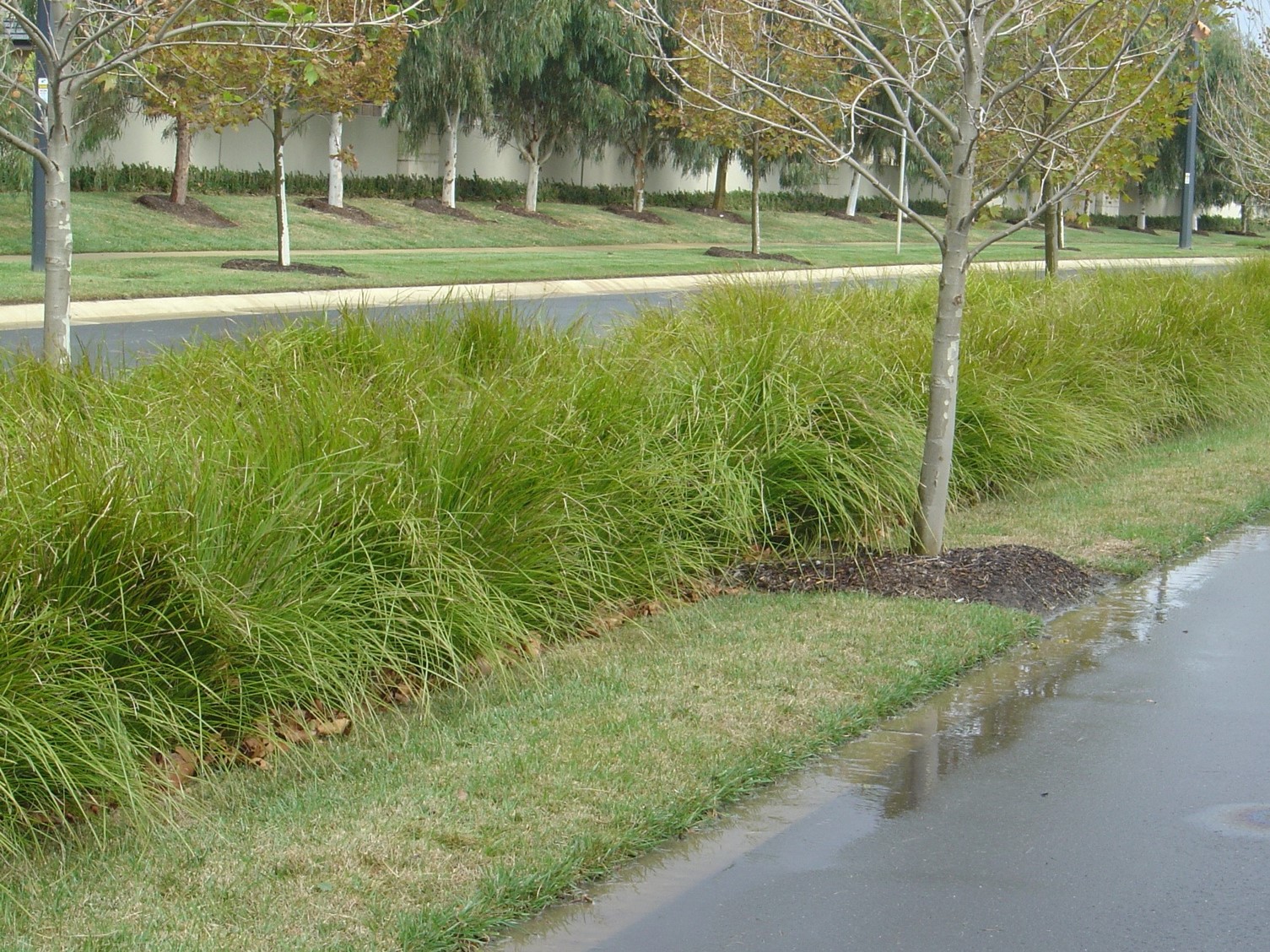

|
国際水環境部門
(2) 水道分野中核人材育成プログラム都市人口の増加と経済開発により、アジア諸都市の水需要が急増しています。これらの都市では、水需要が供給能力を上回り、水不足が深刻化しています。このような水不足を解消するためには、水道事業に関する法制度の整備とともに、水道事業者における人材の育成が急務です。本プログラムでは、アジア開発途上国の水道技術者を大学院修士課程に受入れ、現地の課題解決を通じた人材の育成を行っています。 写真:ラオス首都ヴィエンチャンで開催した水道事業セミナー |
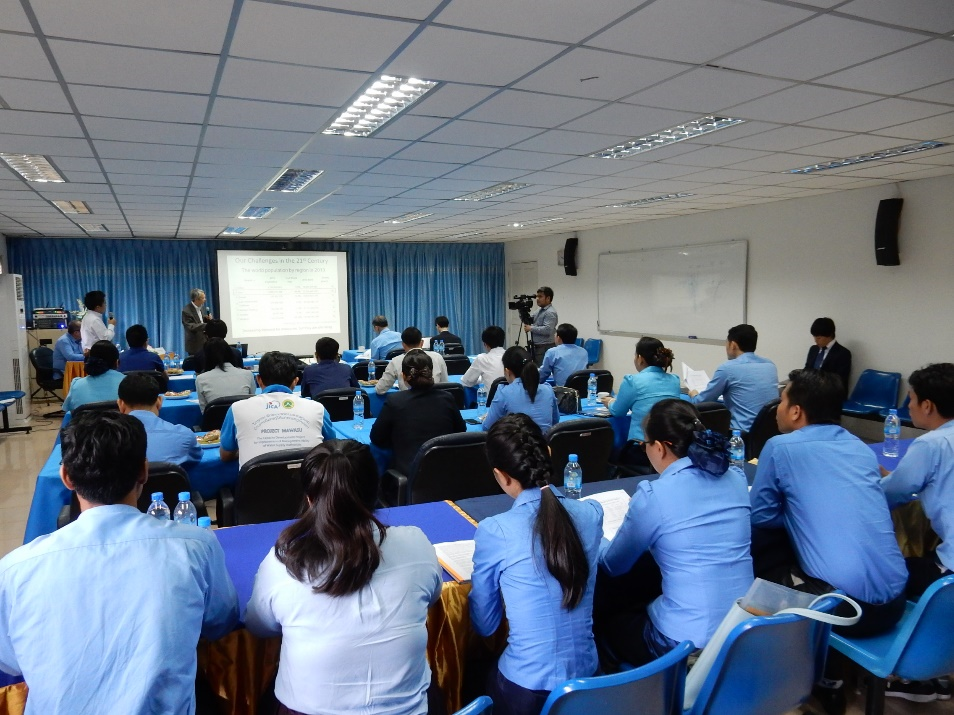

|
(3) 環境管理における適正技術の確立、水安全計画・衛生安全計画の普及安全な飲料水の供給と基本的な衛生設備へのアクセスは、人権として国際的に認められています。給水および衛生施設の実施を促進するためには、地域の状況-技術的、文化的、社会的および経済的側面を考慮することが不可欠です。社会基盤の実装に必要となる「適正技術」、「水安全計画」や「衛生安全計画」のコンセプトを生かしたプロジェクトの推進に関する研究を進めています。 写真: カンボジア郊外での水質調査 |
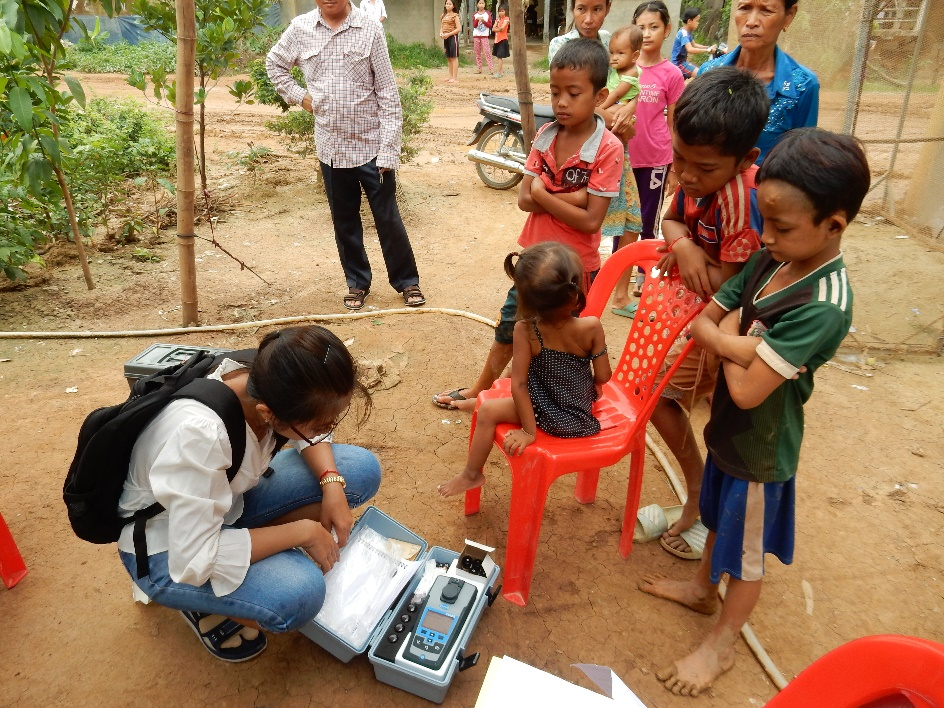

|
Water Quality Control Technologies and Materials Development
(1) Efficient Removal of Viruses and Harmful Substances from Water Using Nanostructured Liquid-Crystalline Polymer MembranesAccess to safe water free of viruses and harmful substances is one of the most important issues worldwide. We are developing nanostructured liquid-crystalline membranes to efficiently remove viruses and other harmful substances from water. These self-organized porous polymer membranes with channels of uniform pore size at the sub-nano or nanometer level have shown to be useful for removal of viruses from water. Photo: A water treatment membrane that purifies water by utilizing the property that liquid crystal molecules have an ordered structure |

|
(3) Management of Organic Matter in the Water Environment considering Water UsageA wide variety of organic matters are discharged from daily life and industry and exist in water environment with natural organic matters. When water is used, certain components are of concern over their toxicity, transformed to disinfection by-products, used as substrates for bacterial regrowth and factors of failures in water treatment. We track organic matters at the molecular species level using high-resolution mass spectrometry for the solutions. Photo: High-resolution mass spectrometry to track organic matters at the molecular species level |

|
Water System Management
(1) Advancement of Urban Flood Risk ManagementAs the frequency of torrential rainfall increases, development of smart urban flood control is required. Therefore, we have been developing next-generation urban flood prediction systems that utilize advanced technologies such as high-resolution radar rainfall observation and real-time sensing of water levels in drainage pipes using manhole IoT. We have conducted research on maximized utilization of inundation countermeasure facilities based on highly accurate flood prediction information, evacuation behavior guidance and inundation prevention plans for damage reduction. Image: A new urban inundation model that comprehensively analyzes water levels in river and drainage systems in the Tsurumi River lowland |

|
(2) Elucidation of Wet Weather Pollution in Urban Coastal AreasWet weather pollution loads include non-point source pollution load derived from road traffic and combined sewer overflows. It is required to evaluate not only pollution by micro-pollutants such as heavy metals and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, but also fecal pollution in the receiving water. Therefore, by elucidating the pollution mechanism using a model and evaluating health risks in the waterfront areas, we have conducted research aimed at predicting pollution derived from combined sewer overflows during wet weather and examining effective countermeasures. Photo: Water sampling in the Tokyo Harbor coastal area after rainfall event |

|
(3) Evaluation of Urban Runoff Control Measures such as Green InfrastructuresIn urban stormwater management, it is important to install infiltration and storage facilities to control urban runoff along with river improvement and drainage works as basin measures. Runoff control facility making use of the green space, so-called Green Infrastructure (GI), has multiple functions such as creating an attractive living space, strengthening inundation measures by slow-down runoff flow, replenishing groundwater, and removing urban runoff pollutants. Therefore, we have conducted research on quantitative evaluation of GI functions using urban water cycle model. Photo: Examples of green infrastructure with runoff control function |

|
International Water Environment
(2) Water Engineering and Utility Management: Future Leaders Training ProgramIn many Asian cities, the water demands have surpassed the supply capacity due to population growth and economic development. To alleviate water shortages, it is necessary to establish laws and regulations on water supply, and develop human resources. In this program, graduate students from Asian countries learn hands-on approaches to solve current problems in water supply engineering and management. Photo: Seminar at water utility in Viang Chan, Lao PDR |

|
(3) Establishing Appropriate Technology in Environmental Management, Water Safety Plans and Sanitation Safety PlanningAccess to safe drinking water supply and basic sanitation has been internationally recognized as human right. In order to facilitate implementation of water supply and sanitation facilities in countries, it is essential to consider their local circumstances, i.e., technical, cultural, social and economic aspects. The research has been conducted on implementation of “Appropriate Technology”, and successful introduction of “Water Safety Plans” and “Sanitation Safety Planning” for water quality management. Photo: Water quality survey in a suburban community, Cambodia |

|